Modern Apartment Living
The Appeal of Modern Apartment Living
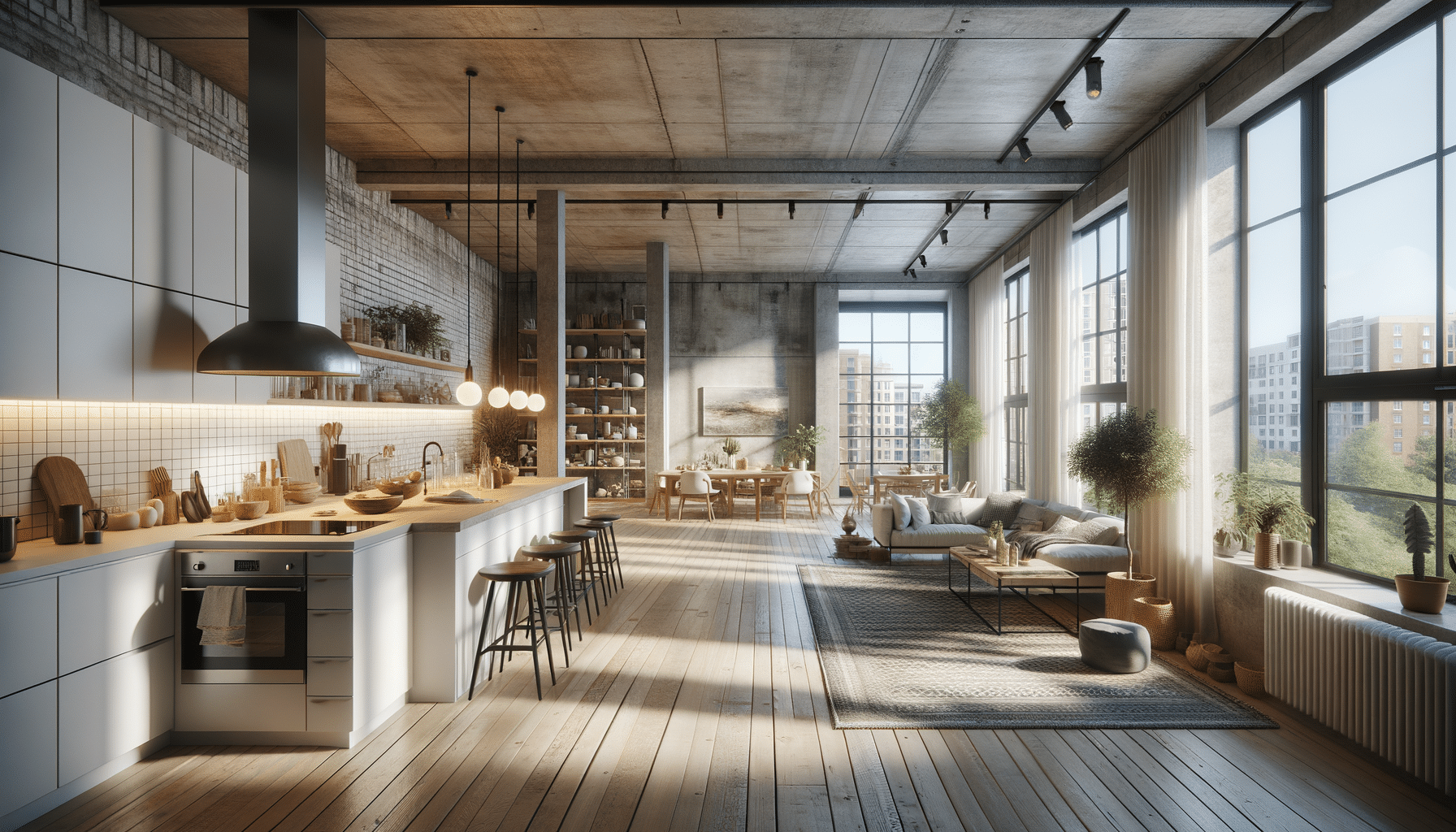
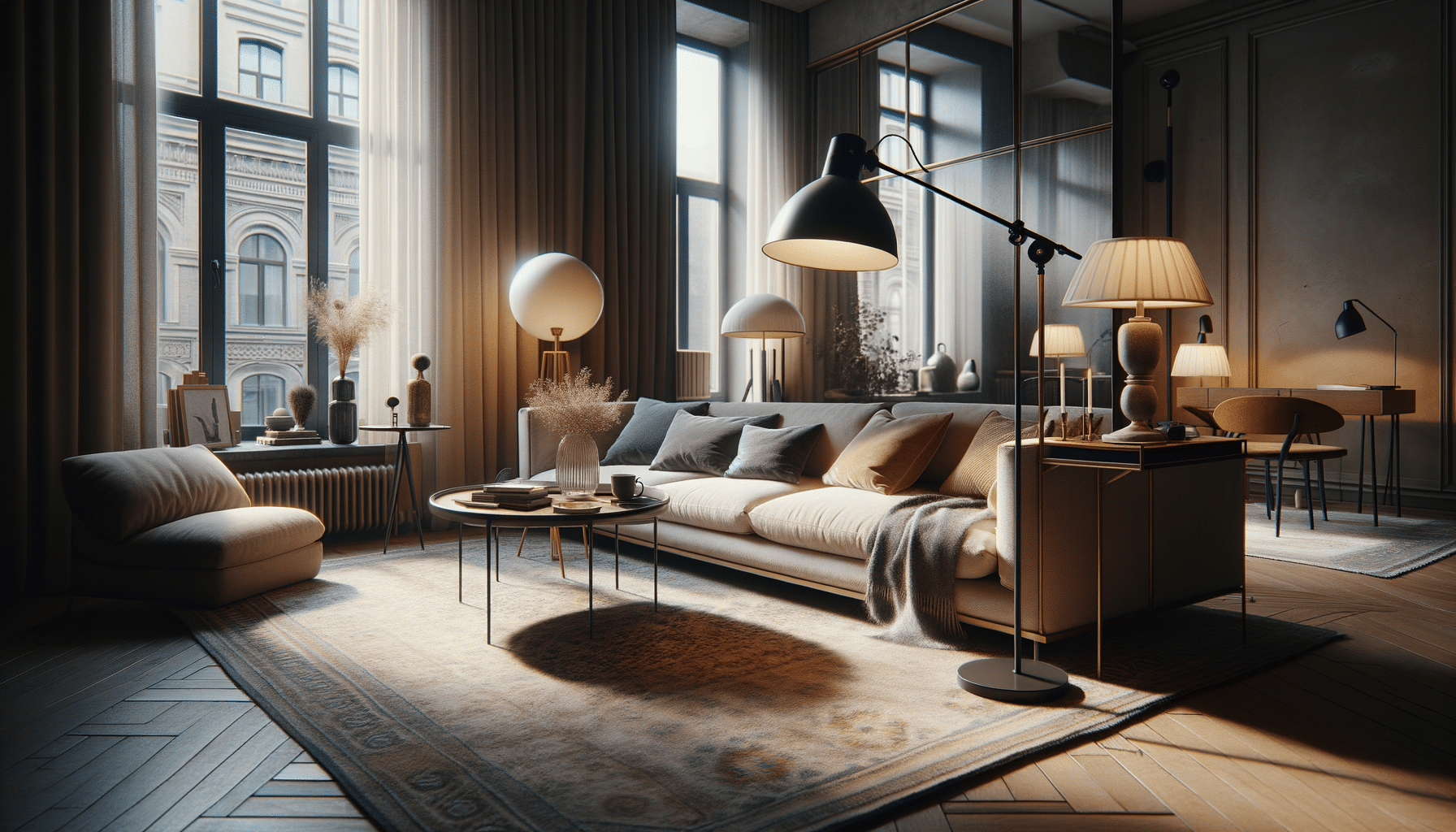
In today’s fast-paced world, modern apartment living has become an increasingly attractive option for many individuals and families. The allure lies in its combination of convenience, style, and functionality. Modern apartments often feature open layouts that maximize space, allowing for a seamless flow between living areas. This design not only enhances the aesthetic appeal but also facilitates a more connected and social living environment. The emphasis on clean, contemporary design elements, such as sleek lines and minimalistic decor, contributes to a sense of tranquility and order, making these spaces ideal for both relaxation and entertaining.
Moreover, modern apartments are typically located in urban centers, providing easy access to amenities such as shopping centers, restaurants, and public transportation. This accessibility reduces the need for long commutes, thereby enhancing the quality of life for residents. The integration of smart home technologies further elevates the living experience, offering convenience at the touch of a button. From energy-efficient appliances to automated lighting systems, these features not only contribute to a sustainable lifestyle but also offer significant cost savings over time.
Design Elements of Modern Apartments
The design elements of modern apartments are characterized by their simplicity, functionality, and elegance. One of the key features is an open floor plan that merges the kitchen, dining, and living areas into a cohesive space. This layout not only maximizes the use of available space but also fosters a sense of community among residents. Large windows are another hallmark of modern apartment design, allowing natural light to flood the interior and create a sense of openness and airiness.
In terms of materials, modern apartments often incorporate a mix of natural and industrial elements. For instance, exposed brick walls and concrete floors can be paired with wooden accents and soft textiles to create a balanced and inviting atmosphere. The color palette tends to be neutral, with whites, grays, and earth tones dominating the decor, providing a versatile backdrop that allows residents to personalize their space with pops of color and texture.
- Open floor plans for seamless flow
- Large windows for natural light
- Mix of natural and industrial materials
- Neutral color palettes with personalized accents
Smart Home Technologies in Modern Apartments
Smart home technologies have revolutionized the way we live, and modern apartments are at the forefront of this transformation. These technologies enhance convenience, security, and energy efficiency, making them an integral part of modern apartment living. For instance, smart thermostats allow residents to control the temperature of their home remotely, ensuring comfort while optimizing energy usage. Similarly, smart lighting systems can be programmed to adjust based on the time of day or occupancy, reducing electricity consumption and enhancing ambiance.
Security is another crucial aspect where smart technologies play a significant role. Modern apartments often come equipped with advanced security systems, including smart locks and surveillance cameras, providing residents with peace of mind. Additionally, voice-activated assistants and integrated home automation systems enable residents to control various aspects of their apartment, from entertainment systems to kitchen appliances, with simple voice commands or through smartphone apps.
- Smart thermostats for energy efficiency
- Advanced security systems with smart locks and cameras
- Voice-activated assistants for home automation
- Smart lighting systems for ambiance and energy savings
Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Features
Sustainability is a key consideration in the design and construction of modern apartments. Developers are increasingly incorporating eco-friendly features to reduce the environmental impact and promote a healthier lifestyle. One of the primary strategies is the use of sustainable building materials, such as recycled steel and reclaimed wood, which minimize resource depletion and waste. Additionally, energy-efficient appliances, solar panels, and water-saving fixtures are commonly integrated into modern apartments to reduce energy consumption and lower utility bills.
Green spaces and rooftop gardens are also becoming popular features in modern apartment complexes. These areas not only provide residents with a connection to nature but also improve air quality and contribute to biodiversity. Furthermore, many modern apartments are designed to be close to public transportation and bike paths, encouraging residents to opt for eco-friendly modes of travel. By prioritizing sustainability, modern apartments offer a living environment that is both comfortable and responsible.
- Use of sustainable building materials
- Energy-efficient appliances and solar panels
- Water-saving fixtures and green spaces
- Proximity to public transportation and bike paths
Community and Lifestyle Benefits
Modern apartment living offers numerous community and lifestyle benefits that enhance the overall living experience. Many apartment complexes feature shared amenities such as fitness centers, swimming pools, and communal lounges, fostering a sense of community among residents. These spaces provide opportunities for social interaction, making it easier for residents to build relationships and engage in community activities.
The lifestyle benefits extend beyond the physical amenities. Living in a modern apartment often means being part of a vibrant urban community with access to cultural events, dining options, and entertainment venues. This proximity to city life allows residents to enjoy a dynamic lifestyle without the need for extensive travel. Furthermore, the maintenance-free living that modern apartments offer is a significant advantage, as it allows residents to focus on their careers, hobbies, and personal growth without the burden of property upkeep.
- Shared amenities like fitness centers and pools
- Opportunities for social interaction and community activities
- Proximity to cultural and entertainment venues
- Maintenance-free living for a stress-free lifestyle